Esophageal stricture due to caustic ingestion is one of the most difficult problems to manage. Esophageal dilations are the usual treatment and they require a great number of sessions in the majority of cases. This implies time, risks for the patient, anguish for the relatives, and very often, frustration for the physician.
ObjectivesTo evaluate the efficacy of the application of topical mitomycin C and intralesional triamcinolone in the prevention of post-dilation esophageal stricture recurrence.
Material and methodsA prospective, comparative, nonrandomized, and longitudinal study was conducted that compared a cohort of 16 patients treated with mitomycin C (2009-2012) with a retrospective cohort of 34 patients treated with triamcinolone (2002-2009).
ResultsThe patients treated with intralesional triamcinolone had a median of 11 dilations (minimum 4 and maximum 24), whereas the median in the patients treated with topical mitomycin C was 4.5 (minimum 3 and maximum 8). The groups were compared using the Mann-Whitney U test, finding a statistically significant difference of a two-tailed P<.001.
In the multiple linear regression model, the dependent variable was the number of dilations and the independent variables were the type of lesion and treatment. The result was an R2 .676 with a significance level of P<.001, in which the regression coefficient for treatment was B −.682 (95% CI −8.286 to −5.025) and the lesion grade was B .435 (95% CI 2.043-4.573).
The ANOVA result was an F 49.08 and a P<.001 and showed that the independent variables of type of lesion and treatment had a linear relation with the number of dilations, reinforcing the fact that our results were not due to chance.
ConclusionsTopical mitomycin C considerably reduced the number of esophageal dilations compared with the use of intralesional triamcinolone to alleviate dysphagia, and therefore we suggest it as a treatment option in strictures due to caustic ingestion.
La estenosis esofágica secundaria a ingestión de cáusticos es uno de los problemas de más difícil manejo. El tratamiento habitual son las dilataciones esofágicas que requiere en la mayoría de los casos un gran número de sesiones, lo cual implica tiempo, riesgos para el paciente, angustia en los familiares y en muchas ocasiones frustración para el médico.
ObjetivosValorar la eficacia de la aplicación de mitomicina C y triamcinolona en la prevención de recurrencia de estenosis esofágica posdilatación.
Material y métodosEstudio prospectivo, comparativo, no aleatorizado y longitudinal en donde se incluyó una cohorte de 16 pacientes tratados con mitomicina C (2009-2012) y se compararon con una cohorte retrospectiva de 34 pacientes tratados con triamcinolona (2002-2009).
ResultadosLa mediana de dilataciones de los pacientes en los que se utilizó triamcinolona intralesional fue de 11 (mínimo 4 máximo 24), mientras que los manejados con mitomicina C tópica fue de 4,5 (mínimo de 3 y máximo de 8). Al comparar estos grupos con U de Mann-Whitney, se encontró que la diferencia es estadísticamente significativa a 2 colas p<0.001.
Al realizarse el modelo de regresión lineal múltiple con variable dependiente el número de dilataciones y variables independientes tipo de lesión y tratamiento se encontró una R2 0.676 con un nivel de significación p<0.001, en donde el coeficiente de regresión para tratamiento fue ≡ –0.682 (IC del 95%, –8.286 a –5.025) y el de grado lesión fue ≡ 0.435 (IC del 95%, 2.043- 4.573).
Anova con una F 49.08 con una p<0.001, lo que demuestra que las variables independientes tipo de lesión y tratamiento observan una relación lineal con el número de dilataciones, lo que refuerza que nuestros resultados no son debidos al azar.
ConclusionesLa mitomicina C tópica redujo considerablemente el número de dilataciones esofágicas en comparación al uso de triamcinolona intralesional para aliviar la disfagia, por lo que la sugerimos como una opción en el tratamiento de las estenosis por cáusticos.
One of the main complications of the ingestion of caustic substances is esophageal stricture. The management of these problems is a difficult and distressing challenge for the patient, the parents, and for the physician in charge of the treatment. Esophageal rehabilitation has been carried out for many years with different techniques, depending on the experience of each physician.1 Esophageal prostheses or splints, dilations with balloons or Savary-Gilliard plugs, Hurst dilators, etc., have been used, but in reality, there is no worldwide standardization for the management of these patients and even less so for the use of certain substances such as triamcinolone acetonide applied intralesionally, or more recently, topical mitomycin C.1,2 Triamcinolone acetonide is a synthetic corticosteroid with a preventive effect on collagen synthesis, fibrosis, and chronic cicatrization that has been used for many years, applied in intralesional injection after esophageal dilations for the purpose of delaying cicatrization and thus reducing the number of dilations.2 Mitomycin C is an antineoplastic and antiproliferative agent that reduces the formation of collagen through fibroblasts and impedes cell duplication. It can delay the cicatrization process in certain tissues, which is why it has been used topically for treating esophageal stricture.3,4 The main aim of this study was to evaluate the number of esophageal dilations required to achieve clinical improvement in a group of patients treated with mitomycin C and another group treated with triamcinolone acetonide.
MethodsA prospective, comparative, nonrandomized, longitudinal study was conducted that included a cohort of 16 patients treated with mitomycin C (2009-2012) and they were compared with a retrospective cohort of 34 patients treated with triamcinolone (2002-2009). The 50 patients were attended to at the zone 6, 66, and 35 hospitals of the Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social in Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua, Mexico. They were diagnosed with esophageal stricture secondary to caustic ingestion and managed with esophageal dilations.
Written statements of informed consent were obtained from the parents of the patients.
In the first 24h after caustic ingestion, upper endoscopy was done to classify the esophageal lesion grade according to the modified Maratka classification5,6 (Table 1).
Classification of caustic esophagitis (Maratka).
| Grade I | Hyperemia and edema |
| Grade II | Yellow or white plaques with pseudomembrane formation |
| II a | Lesions located on one-third of the esophagus and a single wall |
| II b | Concentric lesions located on one-third of the esophagus |
| II c | Linear or concentric lesions in 2 or 3 thirds of the esophagus |
| Grade III | Bleeding and ulcerated mucosa with a thick exudate |
Four weeks after the first endoscopy, a barium esophagogram and endoscopy were carried out, establishing the diagnosis of esophageal stricture.
All the patients included in the dilation protocol presented with some grade of dysphagia that was classified according to the Mellow and Pinkas scale7 (Table 2). Because the cohort was a pediatric one and the majority of the children were preschoolers, the dysphagia was evaluated by the parents, and classified as grade 0: no difficulty in swallowing foods, grade 1: difficulty in swallowing solids (pieces of food), grade 2: difficulty in swallowing soft solids (baby food), grade 3: difficulty in swallowing any type of solid or liquid, and grade 4: difficulty in swallowing saliva (important sialorrhea).
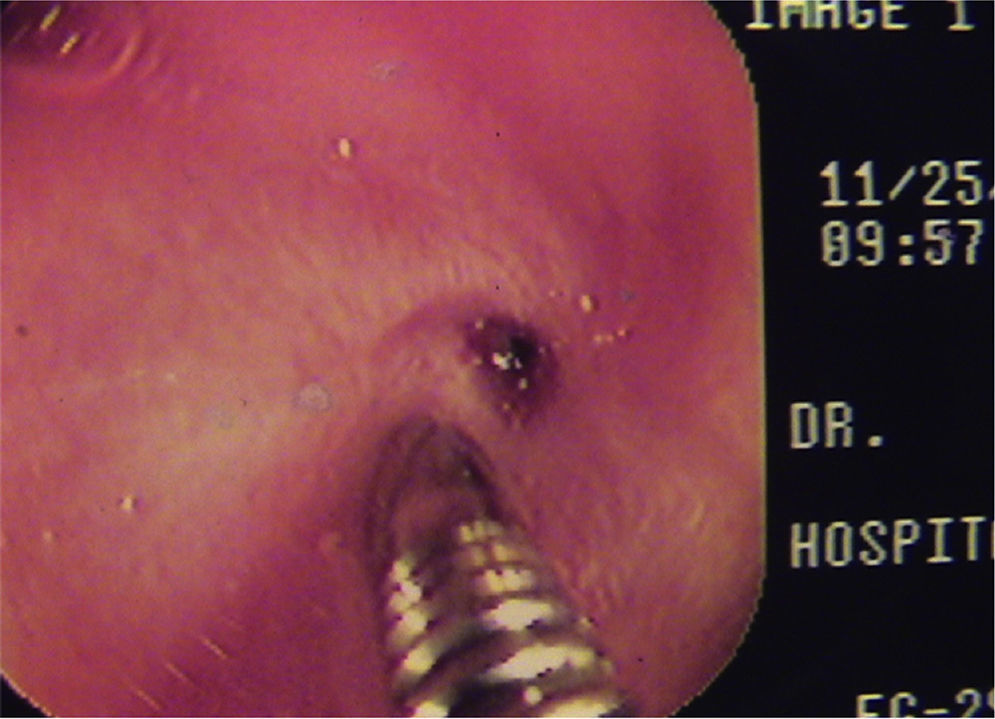
All the esophageal dilations were carried out with the patient under general anesthesia, always administered by a certified pediatric anesthesiologist. The dilations were performed with Savary-Gilliard plugs (flexible and directed plastic dilators), first passing a flexible metallic guidewire through the stricture until reaching the stomach and then passing a different caliber Savary dilator, depending on the diameter of the stricture, through that same space (Fig. 1). After the dilations, we applied intralesional triamcinolone in 4 quadrants. The steroid was applied in the first 5 dilations with an interval of one week between the first and second dilation and then every 2 weeks or more, depending on the clinical and endoscopic response.
In the mitomycin C group, the same dilation technique was followed, after which the medication was applied topically in the first 5 dilations with an interval of one week between the first and second dilation and then every 2 weeks or more, depending on the clinical and endoscopic result.
All the patients were managed with prophylactic oral ranitidine, begun after the first dilation and not suspended until the treatment was finished.
The absence of dysphagia for 6 months after the last dilation was considered good treatment response.
All the patients had follow-up of at least one year after being released from the hospital.
Instruments utilizedSavary-Gilliard dilators of different diameters or French sizes were used (Fig. 2).
A Pentax endoscope of 7.8mm in diameter was used for the first diagnostic endoscopy, the esophageal dilations, and the application of intralesional triamcinolone acetonide.
A Pentax endoscope of 9.0mm in diameter and an operating channel of 2.8mm was used for mitomycin C application.
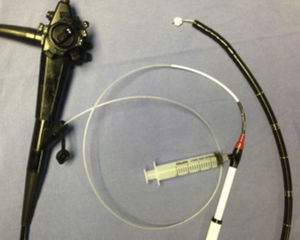
A Dormia basket and cotton swab were used for irrigation (Fig. 3).
Description of the techniqueIntralesional triamcinolone acetonide application:
- 1.
Esophageal dilation under general anesthesia with a Pentax 7.8mm flexible endoscope and Savary-Gilliard dilators.
- 2.
After esophageal dilation the Pentax 7.8mm flexible endoscope was introduced and a sclerotherapy needle was passed through the operating channel to apply the triamcinolone acetonide intralesionally at a concentration of 40mg/ml (1ml of the steroid was diluted in 3ml of sterile water). Always under direct vision, 0.5ml to 1ml was applied per quadrant in the dilated area.
Topical application of mitomycin
- 1.
Esophageal dilation under general anesthesia with Pentax 7.8mm flexible endoscope and Savary-Gilliard dilators.
- 2.
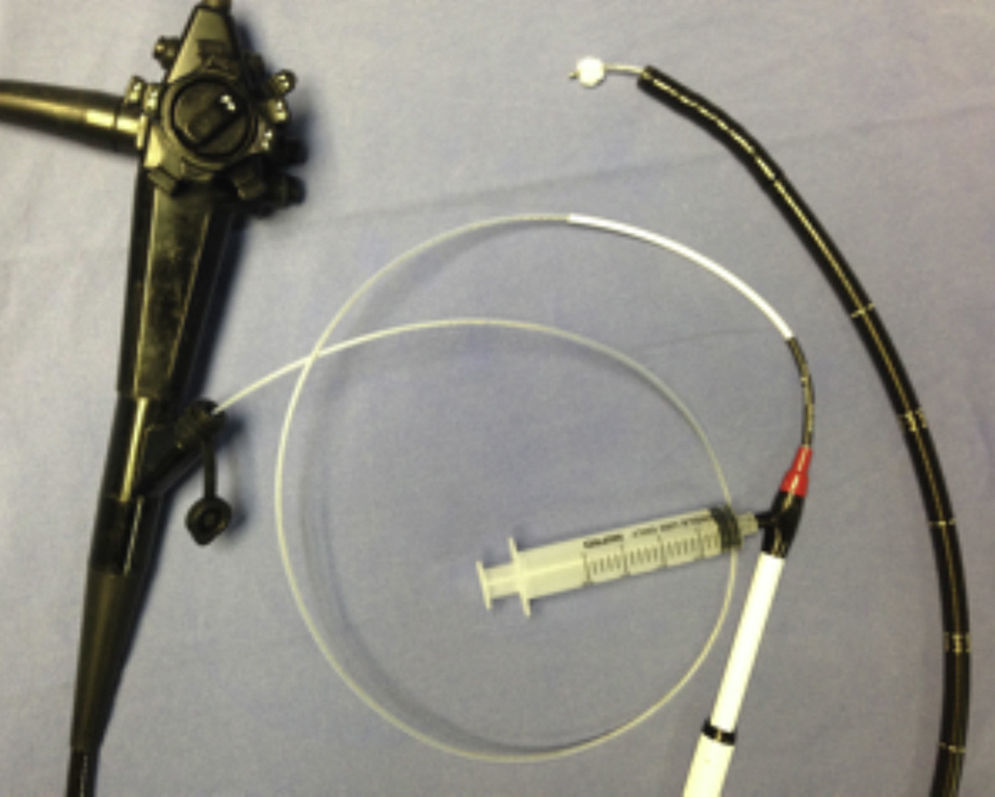
After esophageal dilation the Pentax 9.0mm flexible endoscope with a 2.8mm operating channel was introduced, through which a Dormia basket with a small cotton swab at its tip was passed (Fig. 4).
- 3.
Once the dilated area was located, the Dormia basket irrigator saturated the cotton swab with 2 cc of mitomycin C at a concentration of 0.4mg/ml. Pressure was placed on the eroded mucosa with the swab, thus topically applying the mitomycin C for 3min, always under direct vision (Fig. 5).
Diagnosis and management of all the patients were carried out by the same pediatric gastroenterologist.
Statistical analysisThe SPSS 16 statistical package was utilized. Descriptive statistics were applied using measures of central tendency and dispersion and normality tests for the quantitative variables and frequencies, and percentages for the categorical variables. The group comparisons were performed with the Mann-Whitney U test because the distribution was not normal. Multiple linear regression was carried out with the number of dilations as the dependent variable, and the type of lesion and type of treatment as the independent variables.
ResultsDistribution by sex was 24 females (48%) and 26 males (52%). The median age was 24 months (minimum 11, maximum 148 months). The clinical findings and number of dilations are shown in Tables 3 and 4.
Patients with caustic stricture and application of intralesional triamcinolone.
| Age (months) | Sex | Lesion classification | Dysphagia grade | Number of dilations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 27 | M | II b | 3 | 14 |
| 11 | F | II b | 2 | 9 |
| 23 | F | III | 4 | 24 (3)a |
| 18 | F | II b | 3 | 10 |
| 36 | M | II b | 1 | 7 |
| 26 | M | II b | 1 | 12 |
| 22 | F | II b | 1 | 6 |
| 28 | M | II b | 2 | 8 |
| 27 | F | II b | 2 | 9 |
| 19 | F | II b | 1 | 14 |
| 17 | F | II c | 1 | 11 |
| 20 | M | II b | 1 | 4 |
| 22 | F | III | 3 | 20 (2)b |
| 28 | M | II b | 2 | 12 |
| 18 | F | II c | 3 | 17 |
| 148 | M | II b | 2 | 9 |
| 14 | M | II c | 3 | 14 |
| 32 | M | II c | 4 | 16 (2)b |
| 31 | F | II b | 2 | 10 |
| 48 | F | II b | 3 | 12 |
| 56 | M | II b | 3 | 15 |
| 22 | F | II b | 3 | 12 |
| 12 | M | II b | 2 | 10 |
| 14 | F | II c | 2 | 9 |
| 19 | F | II b | 1 | 11 |
| 28 | M | II b | 1 | 12 |
| 32 | M | II b | 2 | 8 |
| 17 | F | II b | 2 | 14 |
| 12 | M | II c | 1 | 11 |
| 27 | M | II b | 1 | 9 |
| 30 | M | II c | 3 | 15 |
| 24 | F | II b | 3 | 11 |
| 26 | M | II b | 1 | 12 |
| 22 | F | II b | 1 | 10 |
Patients with caustic stricture and application of topical mitomycin C.
| Age (months) | Sex | Lesion classification | Dysphagia grade | Number of dilations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 36 | M | II b | 1 | 4 |
| 22 | M | II b | 3 | 7 |
| 18 | F | II b | 1 | 5 |
| 28 | M | II b | 3 | 8 (2)a |
| 27 | F | II c | 1 | 4 |
| 31 | F | II b | 2 | 3 |
| 38 | F | II b | 1 | 4 |
| 27 | M | II b | 2 | 5 |
| 20 | F | II b | 1 | 5 |
| 19 | M | III | 3 | 7 (2)a |
| 32 | M | II b | 2 | 4 |
| 24 | F | II b | 2 | 5 |
| 22 | M | II b | 1 | 3 |
| 23 | M | II b | 1 | 4 |
| 19 | F | II b | 1 | 4 |
| 31 | M | II c | 3 | 6 |
Alkalis were the cause of the lesion in 46 (92%) cases and acids were the cause in 4 (8%).
At the time of initial diagnosis, 4 patients had 2 esophageal stricture sites and one case had 3 sites.
The results of the Kolmogorov-Smirnov and Shapiro-Wilk normality tests for the variables of age, dysphagia, and number of dilations, grouped according to treatment, showed that age in the mitomycin group was the only variable with normal distribution.
There were no statistically significant differences in the group comparison using the Mann-Whitney U test in relation to age, sex, or dysphagia.
The median of dilations in the patients treated with intralesional triamcinolone was 11 (minimum 4, maximum 24), whereas it was 4.5 (minimum 3, maximum 8) in those managed with topical mitomycin C. In the Mann-Whitney U test group comparison, there was a statistically significant difference of a two-tailed p < 0.001.
In regard to lesion classification, the patients with a grade IIc and III were the ones that in general required a greater number of dilations (Tables 3 and 4).
In the multiple linear regression model, in which the dependent variable was the number of dilations, and the independent variables were the type of lesion and treatment, the result was R2 0.676, with a significant level of p<0.001. The regression coefficient for treatment was B −0.682 (95% CI −8.286 to −5.025) and the lesion grade was B 0.435 (95% CI 2.043-4.573).
The ANOVA result was an F 49.08 and a p < 0.001 and showed that the independent variables of type of lesion and treatment had a linear relation with the number of dilations, reinforcing the fact that our results were not due to chance.
All the patients had a favorable treatment response, defined as the absence of dysphagia and endoscopic improvement for at least 6 months after the last dilation.
No secondary effects were reported with the use of intralesional triamcinolone or topical mitomycin C.
DiscussionCaustic ingestion continues to be a pediatric health problem and the group at greatest risk are children under 5 years of age, with no sex-related predominance, concurring with our results.8,9
Diagnostic endoscopy at the first 24h after the accident is a subject of debate, given that some authors recommend it only if the patient presents with some kind of symptomatology after the caustic ingestion.10,11 In our study, this diagnostic procedure was performed in all the patients because there was no direct correlation in a large number of patients between the clinical findings related to the buccal mucosa and the grade of the esophageal lesion. Therefore, we felt it was important to classify the lesion and in this manner begin patient management, whether with the patient hospitalized, watching for possible complications, or releasing him or her without treatment or with outpatient treatment.12,13
Different therapeutic modalities have been used in an attempt to prevent post-caustic ingestion complications, such as the use of antibiotics, systemic corticosteroids, total parenteral nutrition, nasogastric tubes, anti-acids, splint placement, etc. However, none of them have been shown to be truly effective.14 In our work, we always used antibiotics and systemic steroids, depending on the grade of the esophageal lesion. Nevertheless, as in the majority of the studies published, complications were almost always present.
In the present study, we observed that the patients that developed esophageal stricture, all had at least a IIb lesion. This problem was not found in the patients that had I or IIa lesions. The patients that were the most difficult to manage in relation to the number of dilations were those with a grade III lesion with the Maratka classification. In our literature review we found no study relating esophageal lesion grade according to the Maratka classification with the presence of stricture.
When the patient presents with dysphagia, first an esophagogram is done to evaluate the type of stricture, its location, number, length, etc. In this manner we can plan the commencement of dilations, performing them under fluoroscopy when the strictures are complex.15
We administer a prophylactic acid secretion inhibitor, such as ranitidine, to all patients that undergo an esophageal dilation program, given that these patients can present with gastroesophageal reflux due to esophageal motility alterations secondary to the burn, or present with short esophagus.1,14
Of the 50 patients with esophageal stricture, we observed that 5 of them had more than one stricture at the time of diagnosis and they were the patients that required more dilation sessions.
The majority of patients had short strictures, but it was not possible to obtain that datum in all the patients, and so it was not included in the analysis.
Initial management of esophageal stricture continues to be based primarily on esophageal dilations. In some cases the post-dilation use of substances such as triamcinolone acetonide and mitomycin C has been employed in an attempt to reduce the length of time of treatment.15
Triamcinolone acetonide is a synthetic corticosteroid that has been used in topical, oral, or inhaled forms, or as intra-articular or intramuscular injection as treatment in diverse pathologies with important inflammatory processes. It has been applied for many years in patients with esophageal stricture, as an intralesional injection after the esophageal dilations, for the purpose of delaying cicatrization. However, contradictory study results have been published.14 In our experience, we had moderate results with its use, given that the mean of dilations per patient was practically 12 sessions, signifying a treatment time of up to 2 years.
Mitomycin C is an antibiotic derived from Streptomyces caespitosus. It is an antineoplastic and antiproliferative agent that has been used in different specialities, including oncology, ophthalmology, otorhinolaryngology, and recently in patients with esophageal stricture.15 Its use in the latter pathology varies from article to article, but the large majority state that it is applied topically with gauzes or cotton swabs impregnated with the substance. Others report its use with sprayers or applied through rigid or flexible esophagoscopes at the tip of the hood, to avoid contact of the substance with healthy mucosa.1,12,15 In an effort to find a more practical technique and preventing as much as possible the contact of mitomycin C with healthy mucosa, we developed a new application technique. We apply the substance by means of a Dormia basket and have had good results, concurring with the majority of articles in which its topical use has importantly reduced the number of dilations in patients with difficult-to-manage esophageal strictures. There is no uniform consensus on the number of applications of these medications, given that the published articles describe 1 to 12 applications per patient.1,15 In our 7-year experience, we have used triamcinolone acetonide in the first 5 dilations of each patient with different clinical responses. Due to the poor response of some patients to the use of the intralesional steroid, in 2009 we decided to use topical mitomycin C during the first 5 dilations of each patient and compare its use with that of the steroid. We found that the number of sessions decreased significantly with mitomycin C. Concentrations of mitomycin C have been used from 0.1mg up to 1mg/ml.1,15 In our patients we used a concentration of 0.4mg/ml, as in the majority of the studies, with good results, and we found no secondary effects with its use.
Even though the results showed a clear statistical difference in favor of mitomycin C, our study has the limitation that the cohort was compared with a retrospective one and there was no randomizing. This paves the way for conducting a future randomized, comparative, and prospective study blinded to the evaluator to be able to arrive at definitive conclusions.
ConclusionsIt is difficult to develop the protocol of a study on caustic ingestion and even more so on its complications, given that all patients do not ingest the same substance, the same concentration, nor is it in contact with the mucosa for the same length of time. Nevertheless, in accordance with our study results, we suggest the use of mitomycin C as an alternative in the management of patients with difficult-to-treat esophageal stricture due to caustic ingestion.
Ethical responsibilitiesProtection of persons and animalsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Data confidentialityThe authors declare that they have followed the protocols of their work center in relation to the publication of patient data.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors have obtained the informed consent of the patients and/or subjects referred to in the article. This document is in the possession of the corresponding author.
Financial disclosureNo financial support was received in relation to this study/article.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Please cite this article as: Méndez-Nieto CM, Zarate-Mondragón F, Ramírez-Mayans J, Flores-Flores M. Mitomicina C tópica contra triamcinolona intralesional en el manejo de la estenosis esofágica por cáusticos. Revista de Gastroenterología de México. 2015;80:248–254.