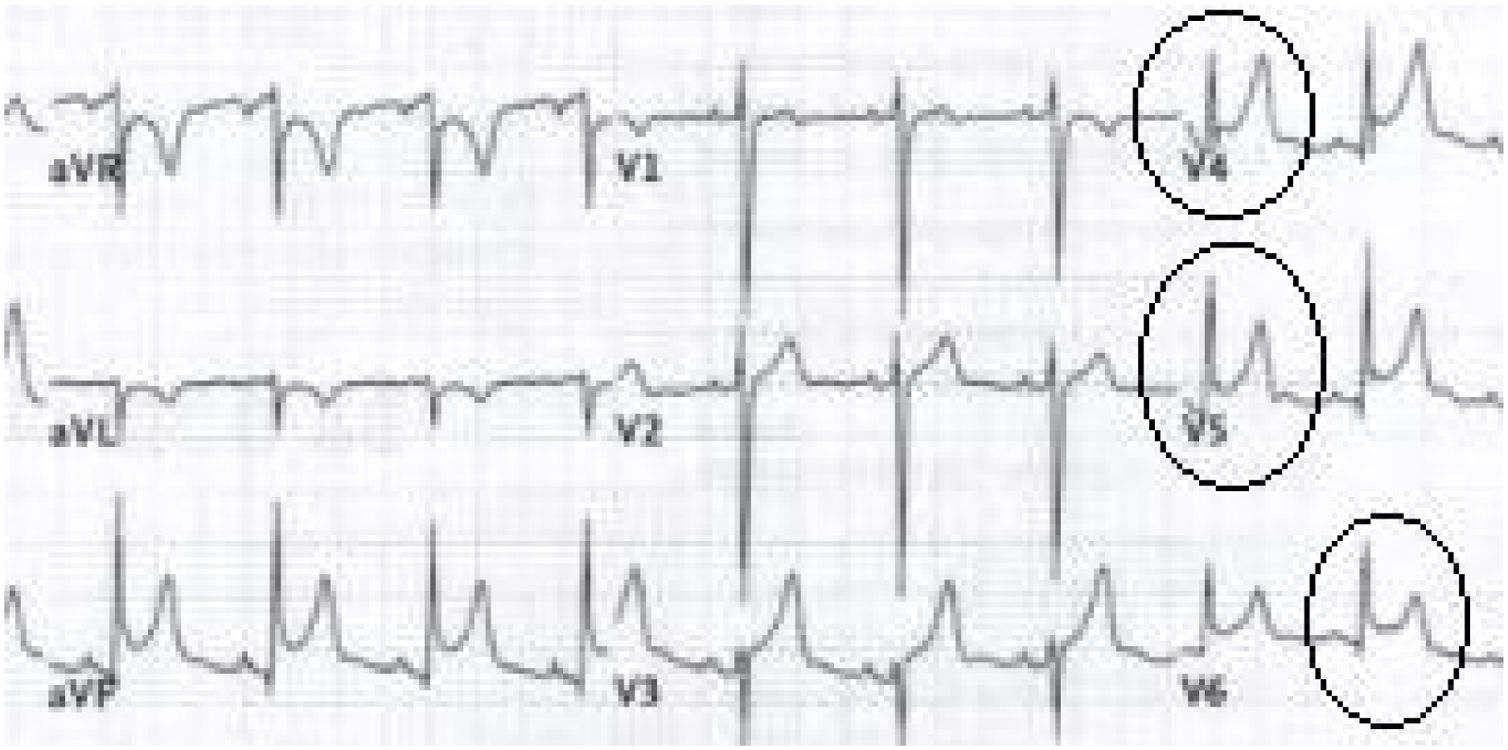
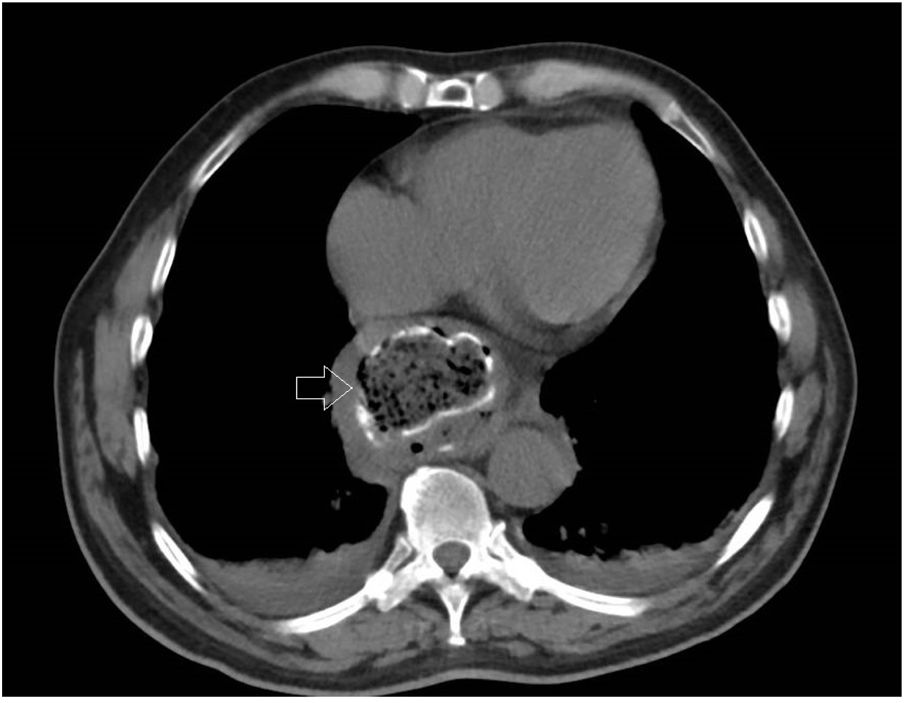
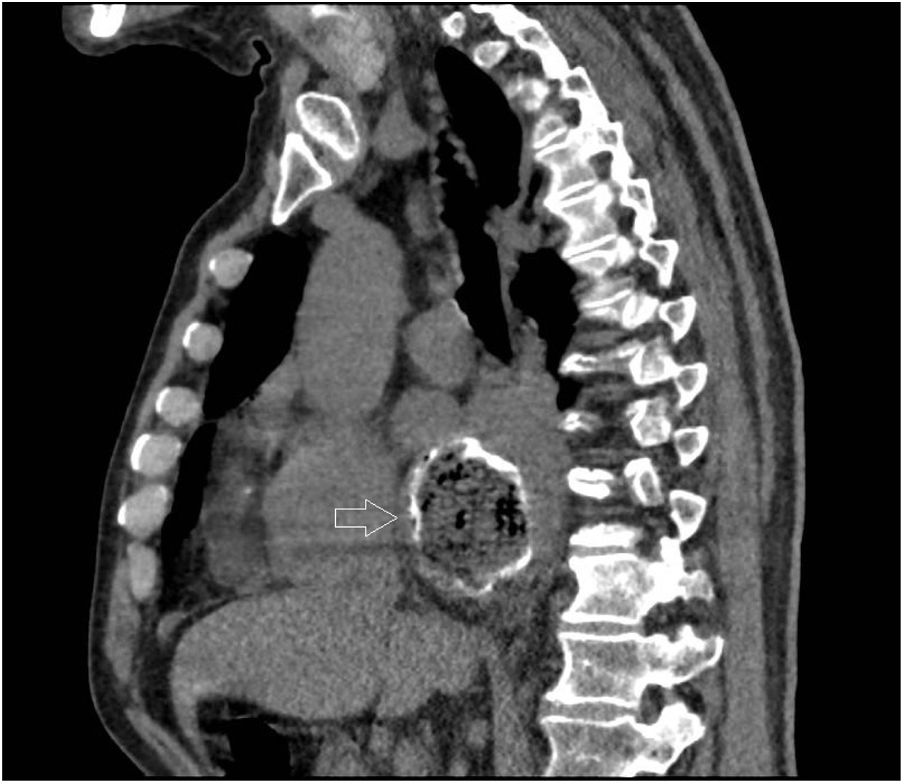
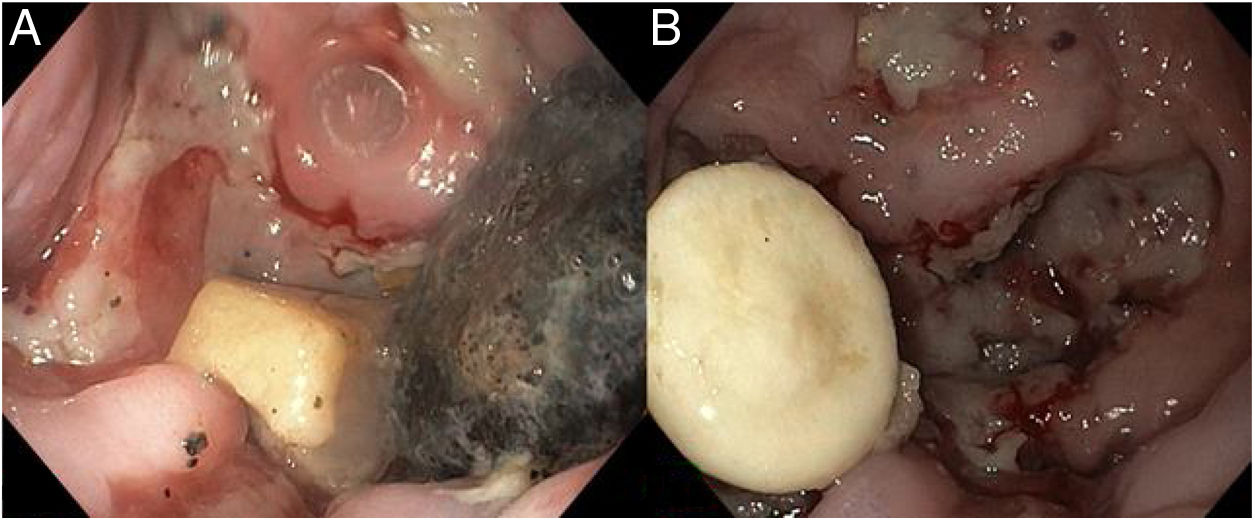
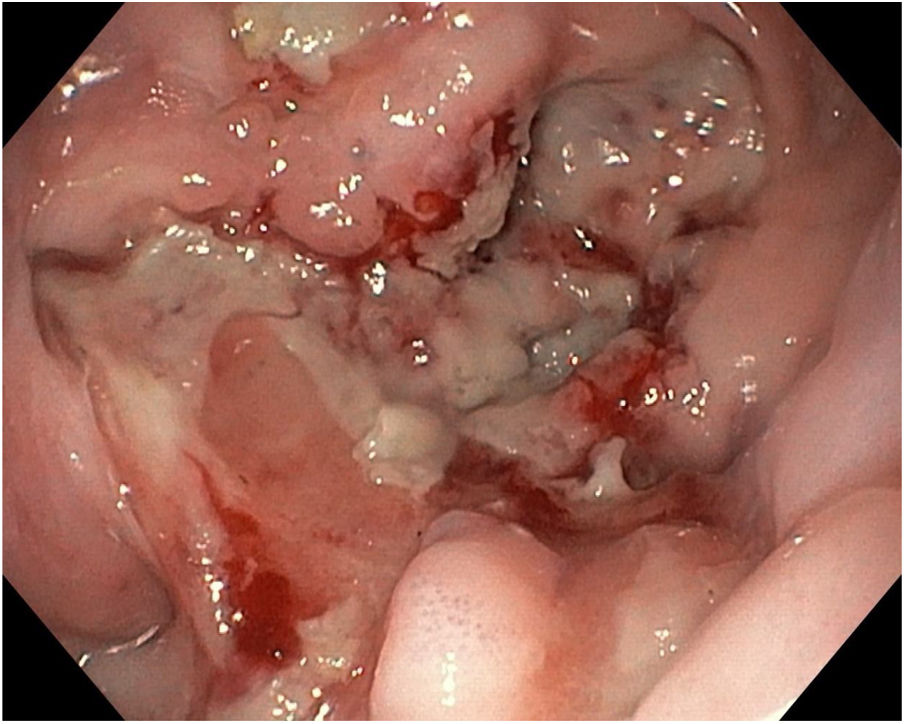
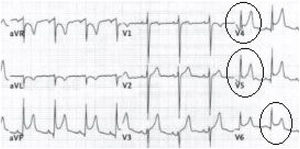
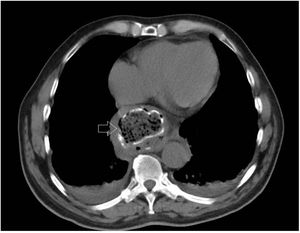
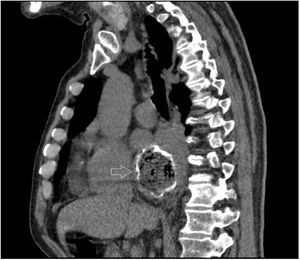
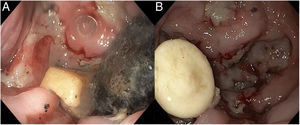
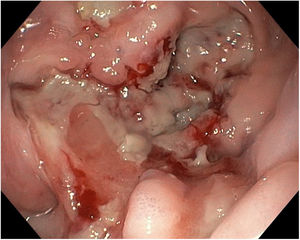
Myopericarditis is a rare disease of predominantly viral etiology but can also be caused by direct or indirect trauma (by contiguity). We present herein the case of a 76-year-old man that sought medical attention for 2-day central chest pain radiating to the scapula, fever, and dysphagia with solids and liquids. An electrocardiogram (Fig. 1) showed ST-segment elevation in the precordial leads. Laboratory test results reported CRP levels of 329.6mg/dl and high troponin levels of 1,695.8pg/mL (normal 0-20). The patient was admitted to the hospital due to suspicion of acute myopericarditis. A chest computed tomography (CT) scan (Figs. 2 and 3) revealed a 55×50mm calcified image located in the esophageal lumen that was dependent on the right esophageal wall, consistent with an epiphrenic diverticulum containing luminal material. Given those findings, the patient’s clinical worsening, and the absence of response to anti-inflammatory drugs, we decided to perform an esophagogastroscopy (Figs. 4A and B). An esophageal diverticulum was identified that contained a plum seed, a pill, and food remnants, all of which were sequentially extracted utilizing a snare. Decubitus lesions were also present in the intra-diverticular mucosa (Fig. 5). The myopericarditis was most likely produced mechanically, due to the fact that the myocardium and pericardium were affected by the transmural inflammation caused by the foreign bodies retained in the diverticulum (Figs. 2 and 3). After their extraction, the patient improved and was discharged 72h later.
Protection of human and animal subjects. The authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this article.
Confidentiality of data. The authors declare that they have followed the protocols of their work center on the publication of patient data.
Right to privacy and informed consent. The authors declare that absolute patient anonymity was preserved in the present article. Informed consent was not requested, given that no personal patient data were published that could identify the patient.
Financial disclosureNo specific grants were received from public sector agencies, the business sector, or non-profit organizations in relation to this article.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Please cite this article as: Ruiz-Rodríguez AJ, Tenorio-González E, Caballero-Mateos AM. Miopericarditis aguda secundaria a cuerpos extraños impactados en divertículo epifrénico. Revista de Gastroenterología de México. 2021;86:193–194.