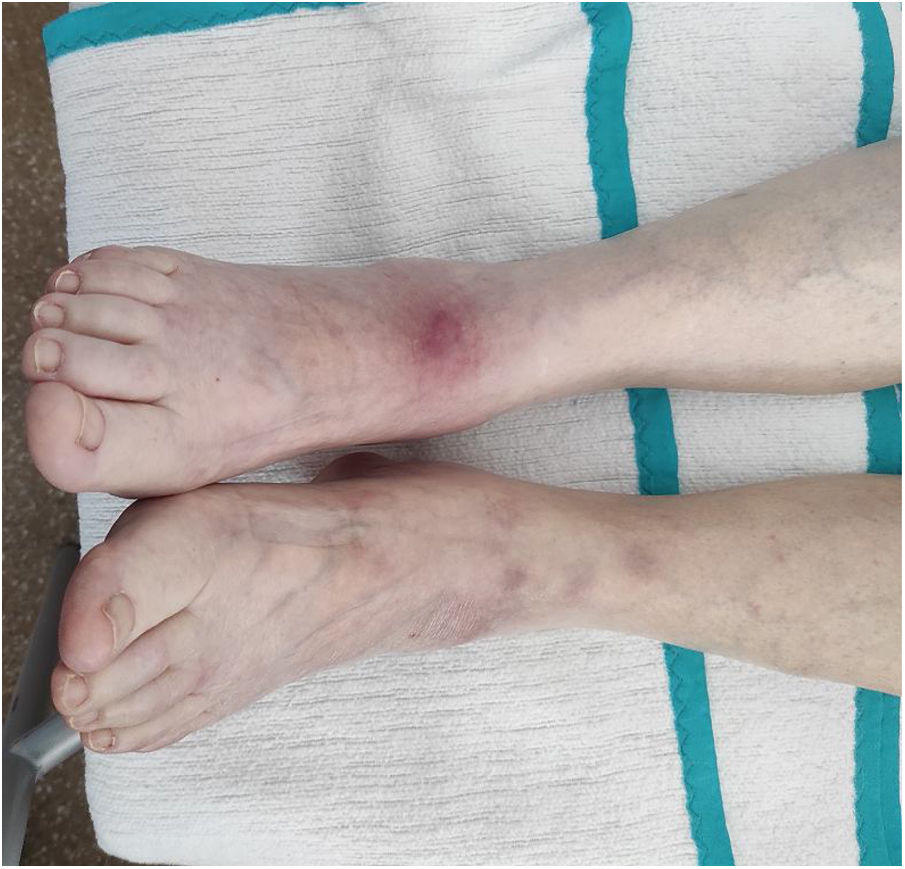
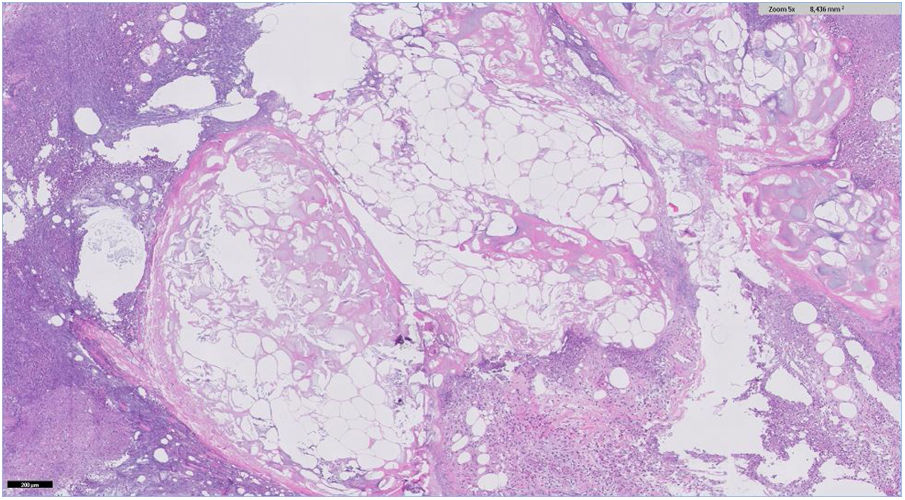
An 83-year-old woman was admitted for acute pancreatitis after consultation for epigastralgia and hyperamylasemia (13,370 U/l; normal range 20-120). Two days later, she presented with nonulcerated, painful, erythematous-purplish subcutaneous nodules on her legs and arms (Fig. 1). Ultrasound revealed inflammation of the subcutaneous cell tissue. A nodule was biopsied and confirmed pancreatic panniculitis (Fig. 2). Pancreatic panniculitis, or pancreatic fat necrosis, is a rare skin manifestation (< 3%) of pancreatic diseases. It can precede the diagnosis of pancreatic pathology, and so pancreatic disease screening should be carried out in patients that present with no abdominal symptomatology. Pancreatic panniculitis is clinically indistinguishable from other types of panniculitis, but the histologic findings are pathognomonic: lobular panniculitis with extensive necrosis of adipocytes and “ghost cells” (adipocytes that have no nucleus and a fine, granular, basophilic deposit due to calcium accumulation). Progression parallels that of pancreatic disease.
The authors declare that:
- ˗
Informed consent was requested of the patient to receive treatment or participate in the study described.
- ˗
The Clinical Image meets the current bioethics research regulations and was authorized by the ethics committee of theHospital Universitario Clínico San Cecilio.
- ˗
This article contains no personal information that could identify the patient.
- ˗
No experiments were conducted on animals or humans.
No financial support was received in relation to this article.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Please cite this article as: Díaz-Alcázar MM, López-Hidalgo JL, Aneiros-Fernández J. La pancreatitis aguda se manifiesta en la piel: paniculitis pancreática. Rev Gastroenterol Méx. 2021;86:309–310.