An association between long-term use of proton pump inhibitors and the development of gastric neuroendocrine tumors has been reported, but it is still a subject of debate. The aims of the present study were to determine the presence of this association in a Mexican population and to identify the risk factors for developing gastric neuroendocrine tumors.
Materials and methodsA case-control study was conducted, in which the cases were patients with a histopathologic diagnosis of gastric neuroendocrine tumor and the controls were patients evaluated through upper endoscopy. The controls were paired by age, sex, and endoscopic examination indication. Proton pump inhibitor use was considered prolonged when consumption was longer than 5 years.
ResultsThirty-three patients with gastric neuroendocrine tumor and 66 controls were included in the study. Eighteen (54.5%) patients in the case group were women, as were 39 (59%) of the patients in the control group. The median age of the patients in the case group was 55 years (minimum-maximum range: 24-82) and it was 54 years (minimum-maximum range:18-85) in the control group. A greater number of patients in the gastric neuroendocrine tumor group presented with gastric atrophy (p<0.0001) and autoimmune atrophic gastritis (p=0.0002), compared with the control group. No association between gastric neuroendocrine tumor and prolonged proton pump inhibitor use, sex, smoking, gastroesophageal reflux disease, Helicobacter pylori infection, diabetes mellitus, or autoimmune diseases was found in the univariate analysis.
ConclusionsThe results of our study showed no association between proton pump inhibitor use for more than 5 years and the development of gastric neuroendocrine tumor. The presence of gastric atrophy and autoimmune atrophic gastritis was associated with gastric neuroendocrine tumor development.
Se ha reportado una asociación entre el uso prolongado de inhibidores de la bomba de protones (IBP) y el desarrollo de tumores neuroendocrinos gástricos (TNE-G), la cual aún es controversial. El objetivo fue determinar esta asociación en nuestra población e identificar los factores de riesgo para el desarrollo de los TNE-G.
Material y métodosEstudio de casos y controles, se incluyeron pacientes con diagnóstico histopatológico de TNE-G, los controles fueron pacientes evaluados con endoscopia superior pareados por edad, sexo e indicación del estudio endoscópico. Se consideró uso prolongado de IBP cuando se utilizó por más de 5 años.
ResultadosSe incluyeron en el estudio 33 pacientes con TNE-G y 66 controles. En el grupo de casos 18 (54.5%) son mujeres y en el grupo control 39 (59%). La mediana de edad es de 55 (rango mínimo-máximo: 24-82) años en el grupo de casos y 54 (rango mínimo-máximo: 18-85) años en el grupo control. En el grupo de los TNE-G se encontró una proporción mayor de pacientes con atrofia gástrica (p<0.0001) y gastritis atrófica autoinmune (p=0.0002) con respecto al grupo control. En el análisis univariado no se encontró asociación entre los TNE-G y el uso de IBP de forma prolongada, sexo, consumo de tabaco, enfermedad por reflujo gastroesofágico, infección por Helicobacter pylori, diabetes mellitus ni enfermedades autoinmunes.
ConclusionesNo se encontró asociación entre el uso de IBP por más de 5 años y el desarrollo de TNE-G. La presencia de atrofia gástrica y gastritis atrófica autoinmune se asociaron al desarrollo de TNE-G.
Gastric neuroendocrine tumors (G-NETs) are rare neoplasias.1 Those tumors proceed from enterochromaffin-like cells of the stomach and have been classified into 4 types, in accordance with their pathophysiology and biologic behavior. Types 1 and 2 are associated with hypergastrinemia and have a low grade of malignancy. Type 2 is related to Zollinger-Ellison syndrome and multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN-1). Types 3 and 4 are gastrin-independent and are more aggressive, produce early metastasis, and have a high proliferation index (Ki-67).1,2 In an epidemiologic analysis conducted in the United States and covering more than 50 years, the incidence of G-NETs was shown to have increased in recent decades, which has been explained by the advent and improvement of endoscopic equipment.3,4
An association has been reported between prolonged proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use and the development of G-NET and appears to be secondary to hypergastrinemia produced by those drugs. Neoplastic regression has also been observed upon the suspension of PPIs.5–9 A study by Brunner et al. was published that included 142 patients treated with pantoprazole (40-160mg/d) for 15 years and they found no increase in the risk for developing G-NET.10 The aim of the present study was to determine whether there was an association between prolonged PPI use and G-NETs, as well as to identify the risk factors for their development.
Materials and methodsA case-control study was conducted at the Instituto Nacional de Ciencias Médicas y Nutrición Salvador Zubirán (INCMNSZ), a tertiary care center, and authorized by the research committee and research ethics committee of that hospital. Patients with G-NET that were seen within the time frame of January 2000 and December 2014 were included. Data were collected from the patient case records and the pathology and gastrointestinal endoscopy archives. Definitive diagnosis was based on the histopathologic and immunohistochemical result. Patients with incomplete case records were excluded.
The controls were patients at the INCMNSZ evaluated through upper endoscopy that did not present with G-NET and selected within the same time frame as the cases. They were paired by age, sex, and endoscopic study indication and 2 controls were used for each case.
PPI use for more than 5 years was considered prolonged, regardless of the type of PPI, dose, or its continuous or intermittent use. The demographic characteristics of the patients were collected, along with a history of smoking, diabetes mellitus diagnosis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, autoimmune diseases, gastric atrophy, Helicobacter pylori infection, G-NET type and stage, and the treatment employed.
Statistical analysisData were expressed as median and minimum-maximum range or proportions. The Mann-Whitney U test was used for comparing medians and the χ2 test or Fisher's exact test for comparing proportions. Statistical significance was set at a p < 0.05. Univariate analysis was carried out to determine the factors associated with the finding of G-NET. The statistical package for the social sciences was employed (SPSS®, version 20.0, Chicago, IL, USA).
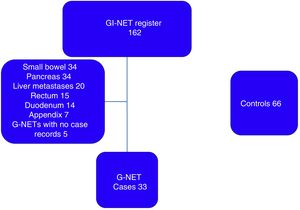
ResultsFrom the 162 patients potentially eligible for G-NET diagnosis, 124 were excluded because their tumors were not located in the stomach and 5 for incomplete case records, resulting in a total of 33 patients with G-NET included in the study (fig. 1). There were 66 controls. Eighteen (54.5%) of the patients in the case group and 39 (59%) in the control group were women. Median patient age was 55 years (minimum-maximum range: 24-82) in the case group and 54 years (minimum-maximum range: 18-85) in the control group.
The main indication for upper endoscopy in both groups was dyspepsia/gastroesophageal reflux. In the G-NET group, there was a greater number of patients with gastric atrophy (p < 0.0001) and autoimmune atrophic gastritis (p=0.0002), with respect to the control group. No association between G-NETs and prolonged PPI use, sex, smoking, gastroesophageal reflux disease, Helicobacter pylori infection, diabetes mellitus, or autoimmune diseases was found in the univariate analysis (table 1).
Comparison of variables between cases and controls.
| Indication | Cases n=33 (%) | Controls n=66 (%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female sex | 18 (54.5) | 39 (59) | 0.666 |
| Age (median, min-max range) | 55 (24-82) | 54 (18-85) | 0.726 |
| Tobacco | 18 (55) | 25 (38) | 0.114 |
| GERD | 7 (21) | 17 (26) | 0.618 |
| PPI > 5 years | 6 (18) | 17 (26) | 0.400 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 5 (15) | 14 (21) | 0.470 |
| Helicobacter pylori | 8 (24) | 20 (30) | 0.527 |
| Autoimmune atrophic gastritis | 8 (24) | 1 (2) | 0.0002 |
| Gastric atrophy | 24 (73) | 4 (6) | < 0.0001 |
| Other autoimmune diseases | 13 (39) | 23 (35) | 0.657 |
| Dyspepsia/GERD | 19 (58) | 38 (58) | > 0.05 |
| Gastrointestinal bleeding | 4 (12) | 8 (12) | > 0.05 |
| Anemia | 8 (24) | 16 (24) | > 0.05 |
| Weight loss | 1 (3) | 2 (3) | > 0.05 |
| Gastric polyposis | 1 (3) | 2 (3) | > 0.05 |
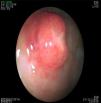
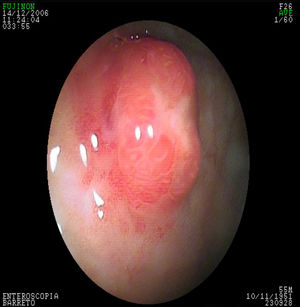
In the G-NET group, 14 (42%) patients had type 1, 6 (18%) had type 2, 5 (15%) had type 3, and type was undetermined in 8 (25%) cases. There were no patients with the type 4 classification. Thirty (91%) patients presented with clinical stage I disease and 3 (9%) with clinical stage II. Treatment was endoscopic in 23 (70%) patients, with 12 (37%) treated in one session and 11 (33%) in several sessions. Nine (27%) patients required surgical treatment and one (3%) patient was untreated (fig. 2).
DiscussionWe evaluated 33 cases of G-NET treated at a referral center. No association was found between prolonged PPI use and G-NETs, coinciding with results of previous studies. The presence of gastric atrophy and autoimmune atrophic gastritis was associated with an increased risk for developing G-NET. The aim of 2 previously published studies on a population with G-NET was to identify the clinical characteristics of those patients. The first was published in 2005 and included 13 patients. Those authors reported that the majority of the tumors were type 1, with low-grade malignancy.11,12 The second was published in 2012, with 31 cases. Tumor location in the stomach was documented in 12 (38.7%) patients and was the most frequent.9,13
Gastric atrophy and autoimmune atrophic gastritis reduce the number of parietal cells and acid production, causing a state of hypergastrinemia. Likewise, PPIs inhibit acid production and cause hypergastrinemia. In what is known as the gastrin hypothesis, hypergastrinemia leads to hyperplasia and dysplasia of enterochromaffin-like cells, microcarcinoid formation, and finally the appearance of G-NET.14,15
A recent Cochrane review reported that long-term treatment with a PPI was associated with hyperplasia of enterochromaffin-like cells (OR: 5.01: 95% CI: 1.54-16.26; p=0.007) but found no relation to the appearance of neoplasias. Previous studies have described similar findings, which could be secondary to the size of the sample or the duration of patient follow-up. G-NETs have a very low prevalence, reported in 0.17/10,000 inhabitants, and so to find associations, studies with larger samples are required. In the cases published, G-NETs have appeared after 12 or more years of treatment with PPIs, and most studies do not include such a long follow-up period.16
The 2 main limitations of our study were its retrospective design and small sample size. Numerous biases due to design can alter results, and in the present study, G-NET prevalence, in particular, could have been underestimated. PPI use was considered prolonged when it was greater than 5 years, regardless of the specific PPI employed, dose, and its continuous or intermittent use, which produced a heterogeneous sample. On the other hand, our analysis included 14 years of study of a rare disease and the sample was one of the largest reported on in the Mexican population.17,18
In conclusion, we found no association between PPIs used for more than 5 years and G-NETs. The presence of gastric atrophy and autoimmune atrophic gastritis were associated with the development of G-NETs.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Financial disclosureNo financial support was received in relation to this study/article.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Please cite this article as: Soto-Solís R, Romano-Munive AF, Santana de Anda K, Barreto-Zuñiga R. Factores relacionados a tumores neuroendocrinos gástricos. Revista de Gastroenterología de México. 2019;84:52–56.