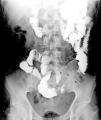
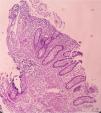
A previously healthy 48-year-old man came to the emergency service presenting with diffuse abdominal pain of three-month progression, associated with periods of diarrhea, bloating, and weight loss of approximately 10kg. Upon admission, his vital signs were within normal parameters and abdominal examination showed no peritoneal irritation, masses, or visceromegaly. A calprotectin stool test reported fecal calprotectin of 2,351μg/g (reference value:<50μg/g) and a lower gastrointestinal barium x-ray revealed filiform contrast medium passage at the level of the ileum (string sign) (Fig. 1). During colonoscopy, active ulcerative ileitis was observed, with a polyp at the mouth of the ileocecal valve. The anatomopathologic study reported mild diffuse chronic inflammation (Fig. 2). Given the diagnostically inconclusive results, magnetic resonance enterography was performed, and the findings were consistent with Crohn’s disease (CD) (Fig. 3 A and B). Treatment for moderate ileal CD was indicated: induction therapy with oral steroids and the later addition of thiopurines for remission maintenance. At three months of follow-up, the patient experienced symptom improvement, weight gain, and the absence of flare-ups.
Intestinal transit, anteroposterior view of the abdomen 50 minutes after oral contrast medium administration, showing adequate passage through the duodenum and jejunum. Sudden narrowing of the caliber of the ileal lumen is visualized in a 10cm tract, identifying filiform contrast medium passage, with the anteroposterior diameter measuring 1.5mm (string sign) (arrows), suggestive of Crohn’s disease.
Magnetic resonance enterography, BTFE sequence: A) axial view, B) coronal view. Severe thickening and parietal stratified-looking edema of the terminal ileum (arrow heads) with thickness up to 20mm and length of 10cm, conditioning luminal narrowing (arrow) with 98% stricture, associated with edema of the mesenteric fat. The MaRIA scoring system was employed, adding the individual scores of the six segments (rectum, sigmoid colon, descending colon, transverse colon, ascending colon, and ileum), obtaining a global index of 3 points.
The authors declare that informed consent was obtained from the patient. The present work meets the current bioethics research regulations and was approved by the institutional ethics committee. The authors declare this work contains no information that could identify the patient and guarantees the right to privacy and preservation of anonymity of the patient. No experiments on animals or humans were conducted.
Financial disclosureNo financial support was received in relation to this article.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.