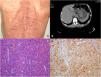
A 65-year-old man presented with abdominal pain and weight loss over a period of 3 months.
His past medical history included hypertension and neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1). Physical examination was notable for multiple cutaneous nodules and café-au-lait spots of the skin distributed over the entire body (Fig. 1A). Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy and abdominal computed tomography scan revealed a tumor mass originating from the anterior wall of the gastric antrum with an intraluminal growth pattern (fig. 1B). The patient underwent distal subtotal gastrectomy. Histopathological examination revealed an epithelioid cell type tumor (Fig. 1C) with >10 mitoses per 50 high power fields. Immunohistochemical examinations revealed tumor cell positivity for CD117/KIT (Fig. 1D) and CD34. NF1 (von Recklinghausen disease) is an autosomal-dominant disorder occurring in one out of every 3,000 births. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) are mesenchymal tumors that are the most common gastrointestinal manifestation of NF1. The proximal jejunum is the most common site of GISTs in patients with NF1, and these tumors tend to be multiple. NF1-associated gastric GIST is an extremely rare event and fewer than 20 cases have been reported to date. Surgical resection with disease-free microscopic margins and an intact pseudocapsule is first-line treatment. In NF1-associated GIST, KIT and PDGFRA mutations are frequently absent and imatinib is ineffective.
(A) Image of the patient showing multiple neurofibromas and café-au-lait spots on the back. (B) Abdominal computed tomography scan documenting a 7.8 × 5.2 cm endoluminal mass in the stomach. (C) Epithelioid variant of GIST (H&E, ×100). (D) Immunohistochemistry of tumor cells (DAB, ×100) showing diffuse membranous immunoreactivity for CD117/KIT.
The authors declare that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form, the patient has given his consent for his images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. The patient understands that his name and initials will not be published, and due efforts will be made to conceal his identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed
Financial disclosureNo financial support was received in relation to this article.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that there is no known conflict of interest.